hand skin sensitivity - treatment of sensitive skin on hands
The sensitivity of the skin of the hand is a common concern that affects many people, from those frequently washing their hands to individuals with naturally dry or atopic skin. Understanding why the skin on your hand feels so sensitive, recognizing the early and advanced symptoms, and knowing how to prevent or treat hand skin sensitivity are essential steps for maintaining healthy skin. By exploring the causes, signs, prevention methods, and treatment options, you’ll gain clear, science-backed insights that go beyond generic advice. This comprehensive approach ensures that you don’t just manage symptoms temporarily but achieve lasting relief and healthier, more resilient hands.
Causes of Hand Skin Sensitivity
Causes of Hand Skin Sensitivity usually develop as a result of a weakened skin texture combined with repeated exposure to environmental irritants. Frequent contact with harsh detergents, alcohol-based products, chemical solvents, hot water, and even prolonged exposure to water can strip away the skin’s natural lipids, creating the ideal conditions for hand skin sensitivity to appear. In dermatological science, this process is commonly classified as irritant contact dermatitis, a condition associated with redness, dryness, scaling, and a burning or stinging sensation, and it tends to be more pronounced in individuals with dry or atopic skin types.
Causes of Hand Skin Sensitivity are not limited to external triggers, as immune-mediated responses also play a significant role in certain individuals. Contact with substances such as latex, metals like nickel, or cosmetic preservatives may provoke allergic contact dermatitis, further intensifying hand skin sensitivity through inflammatory immune pathways. Environmental factors including low humidity, temperature fluctuations common in colder Canadian climates, excessive hand washing, and chronic stress are recognized entities that disrupt cellular repair mechanisms and amplify cutaneous inflammation, ultimately accelerating the sensitization process of the skin on the hands.
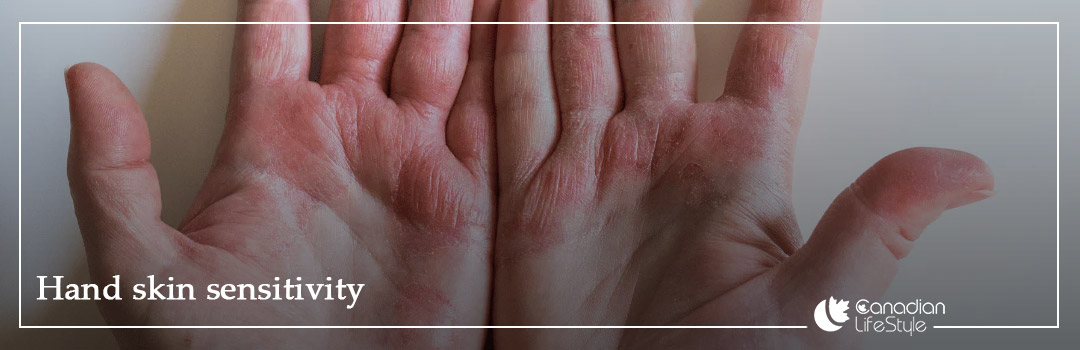
Symptoms of Hand Skin Sensitivity
Symptoms of Hand Skin Sensitivity typically begin with a combination of visible and sensory changes, most commonly redness, pronounced dryness, persistent itching, and a burning or stinging sensation. These manifestations arise from inflammation of the epidermal layer and impairment of the skin’s protective barrier, and they are widely recognized in clinical dermatology as early indicators of hand skin sensitivity. Additional signs such as flaking, abnormal roughness, and superficial fissures result from moisture depletion and the loss of natural skin lipids, often becoming more noticeable after exposure to cleansing agents or cold, dry weather conditions common in many parts of Canada.
Symptoms of Hand Skin Sensitivity may progress over time and present in more severe forms, including swelling, painful cracks, skin thickening, or the development of small, fluid-filled blisters, which are frequently associated with contact dermatitis or cutaneous allergic reactions. In these advanced stages, hand skin sensitivity reflects an activated immune response driven by repeated exposure to allergens, sensitizing metals, chemical irritants, or excessive hand washing. Such symptoms indicate heightened skin inflammation and disrupted cellular renewal, signalling the need for targeted dermatological care .
Prevention Methods for Hand Skin Sensitivity
Prevention Methods for Hand Skin Sensitivity are primarily based on protecting the skin structure of the hands, minimizing exposure to irritants, and maintaining optimal moisture balance. Regular use of topical formulations containing ceramides, urea, dexpanthenol, and vitamin E supports lipid barrier restoration and strengthens the epidermis, helping reduce dryness and pruritus associated with hand skin sensitivity. In addition, gentle cleansing with lukewarm water and sulfate-free soaps, limiting contact with harsh detergents and allergens, and thoroughly drying the hands after washing are evidence-based strategies that reduce barrier disruption and lower the risk of irritation. Regular use of moisturizing and hydrating cream prevents increased sensitivity of the skin on the hands.
Prevention Methods for Hand Skin Sensitivity also include behavioural and environmental measures that limit cumulative skin damage over time. Wearing protective gloves during dishwashing, gardening, chemical handling, or during cold Canadian winters, avoiding prolonged water exposure, and consistently applying a targeted barrier-repair hand cream help preserve skin integrity and control hand skin sensitivity. When practiced consistently, these preventive approaches decrease inflammatory flare-ups, reduce the occurrence of painful fissures, and support long-term hand skin resilience. Treatment of Hand Skin Sensitivity
Treatment of Hand Skin Sensitivity depends on symptom severity and underlying causes, but clinically effective management focuses on reducing exposure to irritants, restoring the skin barrier, and controlling inflammation. The use of formulations enriched with ceramides, urea, dexpanthenol, and vitamin E supports epidermal repair and replenishes natural moisture, helping to relieve dryness, itching, and erythema associated with hand skin sensitivity. Gentle cleansing routines, along with wearing protective gloves when handling detergents or allergens, play a preventive and therapeutic role, while careful selection of hypoallergenic cosmetic and personal care products reduces the risk of further sensitization.
Treatment of Hand Skin Sensitivity in moderate to severe or persistent cases may require short-term use of mild topical corticosteroids under medical supervision to rapidly calm inflammation and pruritus. When pharmacological care is combined with preventive strategies—such as avoiding known triggers, using non-irritating cleansers, and applying a daily barrier-repair hand cream—the recovery process becomes more efficient and long-lasting. This integrated approach minimizes flare-ups and helps stabilize hand skin sensitivity, particularly in environments with frequent hand washing or cold, dry Canadian climates.It is recommended that you find the cause of dry skin after bathing and fix it before an allergy develops.
How to treat sensitive skin on hands?
- Limit contact with harsh cleansers, alcohol-based sanitizers, and hot water, and switch to sulfate-free, pH-balanced cleansers to prevent further barrier disruption.
- Use protective gloves during cleaning, outdoor exposure, or cold Canadian weather to minimize inflammation triggered by low humidity and temperature changes.
- In persistent cases, short-term use of mild anti-inflammatory topical treatments under medical guidance can help control redness, itching, and reactive symptoms.
Why does the skin on my hand feel so sensitive?
This sensation often develops when the skin’s protective barrier becomes compromised, allowing irritants and allergens to penetrate more easily and trigger inflammation. Frequent hand washing, exposure to harsh cleansers, alcohol-based sanitizers, cold weather, and low humidity can strip away essential lipids and natural moisturizing factors, leading to increased transepidermal water loss. As a result, nerve endings in the epidermis become more reactive, which explains the burning, stinging, or tight feeling commonly reported in cases of hand skin sensitivity. From a dermatological perspective, this process is closely linked to barrier dysfunction and early-stage irritant contact dermatitis.
Why does the skin on my hand feel so sensitive? In some individuals, the answer also lies in immune system activation and individual skin type. People with dry, atopic, or genetically predisposed skin tend to have a weaker lipid matrix and reduced ceramide levels, making them more vulnerable to inflammatory responses. Environmental stressors such as seasonal temperature changes, occupational exposure to chemicals, and chronic psychological stress can further amplify inflammatory pathways, prolonging symptoms and delaying cellular repair. Over time, these combined factors intensify hand skin sensitivity, especially in climates with long winters and frequent hand hygiene practices, such as those commonly experienced across Canada.
What causes you to have sensitive hand touch?
Internal factors also play a meaningful role in hand skin sensitivity, including genetic predisposition, dry or atopic skin types, and immune-mediated inflammatory responses. Contact with allergens such as nickel, latex, or certain preservatives may trigger allergic contact dermatitis, while chronic stress and frequent hand washing can disrupt cellular repair mechanisms and prolong inflammation. In colder Canadian climates, low humidity and seasonal temperature shifts further exacerbate nerve reactivity, accelerating the onset and persistence of hand skin sensitivity by impairing normal skin regeneration.
skin sensitivity on hand and arm
Skin Sensitivity on Hand and Arm can also be influenced by systemic and individual factors. People with atopic or dry skin, or those genetically predisposed to barrier weakness, are more susceptible to inflammatory responses from allergens like nickel, latex, or chemical preservatives. Additional stressors such as low humidity, cold weather, excessive hand washing, and chronic stress amplify cutaneous inflammation and delay barrier recovery. Consistent use of barrier-repair creams, protective gloves, and gentle cleansing routines can help restore skin integrity and reduce hand skin sensitivity along the forearm.
Why is the skin on my arm suddenly sensitive?
Sudden sensitivity on the arm typically occurs when the skin tissue is acutely disrupted, allowing irritants or allergens to overstimulate sensory nerve endings. Triggers such as harsh soaps, chemical cleaners, detergents, insect bites, or prolonged exposure to hot or cold temperatures can strip natural lipids and moisture from the epidermis, leading to redness, itching, or a stinging sensation. Clinically, this rapid onset is often linked to irritant contact dermatitis or an acute inflammatory response associated with hand skin sensitivity extending up the arm.
Why is the skin on my arm suddenly sensitive? Allergic reactions may also be responsible, where exposure to metals like nickel, latex, certain skincare products, or fragrances provokes an immune-mediated response. Stress, sudden environmental changes, and low humidity—common in Canadian winters—can exacerbate inflammation and delay recovery. When combined with pre-existing dry or atopic skin, these factors intensify hand skin sensitivity and may cause the discomfort to appear suddenly along the arm as well.
Conclusion
Hand skin sensitivity is a multifactorial condition influenced by both external irritants and internal physiological factors. Weakening of the skin barrier through repeated exposure to harsh chemicals, detergents, extreme temperatures, or low humidity, combined with immune responses and genetic predisposition, can lead to redness, dryness, itching, and discomfort. Early recognition of symptoms, such as stinging, flaking, or tactile hypersensitivity, is essential for effective management and prevention. To reduce hand skin sensitivity, use our specialized products to reduce symptoms and speed up treatment with effective herbal ingredients.